一、什么是IO流
输入流和输出流。
- 输入流:数据从数据源(文件)到程序(内存)的路径
- 输出流:数据从程序(内存)到数据源(文件)的路径
二、常用的文件操作
学习目标:创建文件对象相关构造器和方法
new File(String pathname)//根据路径构建一个File对象
new File(File parent,String child)//根据父目录文件 子路径构建
new File(String parent,String child)//根据父目录 子路径构建
学习任务:在e盘下,创建文件news1.txt、news2.txt、news3.txt用三种不同方式创建。
三种方式简单看一下就行,后面会经常遇到。
new File(String pathname)//根据路径构建一个File对象
package com.file;
import java.io.*;
public class FileCreate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//方式 1 new File(String pathname)
String filePath = "e:\\news1.txt";
File file = new File(filePath);
try {
//创建新文件
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("文件创建成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}new File(File parent,String child)//根据父目录文件 子路径构建
package com.file;
import java.io.*;
public class FileCreate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//方式 2 new File(File parent,String child) //根据父目录文件 子路径构建
//e:\\news2.txt
File parentFile = new File("e:\\");
String fileName = "news2.txt";
//这里的 file 对象,在 java 程序中,只是一个对象
//只有执行了 createNewFile 方法,才会真正的,在磁盘创建该文件
File file = new File(parentFile, fileName);
try {
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("创建成功~");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}new File(String parent,String child)//根据父目录 子路径构建
package com.file;
import java.io.*;
public class FileCreate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//方式 3 new File(String parent,String child) //根据父目录 子路径构建
String parentPath = "e:\\";
String fileName = "news3.txt";
File file = new File(parentPath, fileName);
try {
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("创建成功~");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}三、获取文件的相关信息
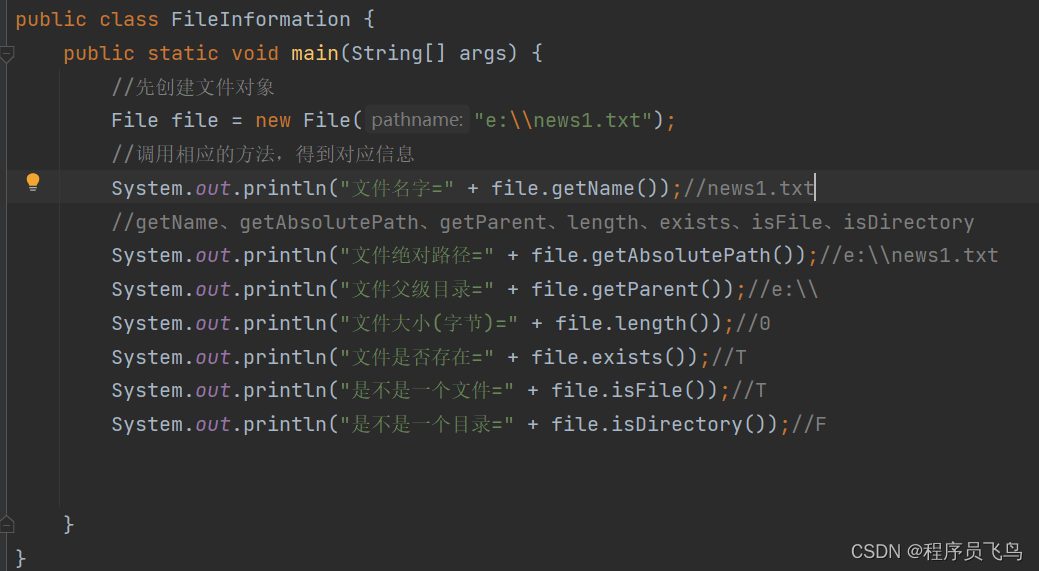
getName、getAbsolutePath、getParent、length、exists、isFile、isDirectory
学习任务:获取文件的大小、文件名、路径、父File,是文件还是目录(目录本质也是文件,一种特殊的文件),是否存在
四、目录的操作和文件删除
学习任务:
- 判断e:\news1.txt是否存在,如果存在就删除
- 判断e:\\demo02是否存在,存在就删除,否则提示不存在
- 判断e:\\demo\a\b\c目录是否存在,如果存在就提示已经存在,否则就创建
package com.collection;
import java.io.File;
public class Delete {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath="e:\\news1.txt";
File file=new File(filePath);
if(file.exists()){
file.delete();
}else {
System.out.println("否则文件不存在~");
}
}
}package com.collection;
import java.io.File;
public class Delete {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath="e:\\demo02";
File file=new File(filePath);
if(file.exists()){
if(file.delete()){
System.out.println(filePath "删除成功");
}
else{
System.out.println(filePath "删除失败");
}
}else {
System.out.println("否则目录不存在~");
}
}
}package com.collection;
import java.io.*;
public class Delete {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String directoryPath="e:\\demo\\a\\b\\c";
File file=new File(directoryPath);
if(file.exists()) {
System.out.println(directoryPath "存在。。");
}
else {
if (file.mkdirs()){
System.out.println(directoryPath "创建成功。。");
}else{
System.out.println(directoryPath "创建失败。。");
}
}
}
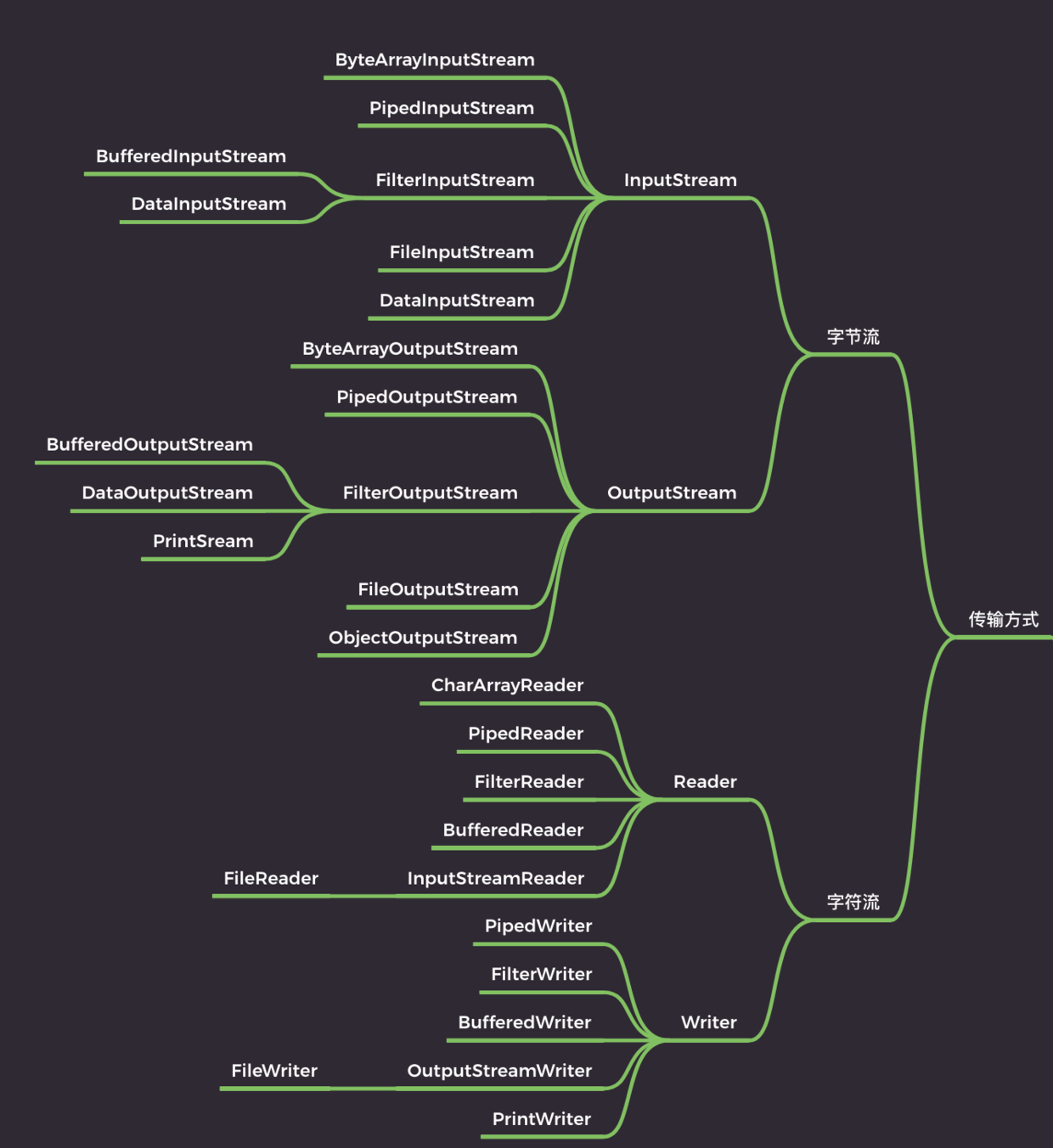
}按操作数据单位不同分为:字节流(8bit)二进制文件,字符流(按字符)文本文件
按数据流的流向不同分为:输入流,输出流
按流的角色的不同分为:节点流,处理流/包装流
字节流:InputStream,OutputStream
字符流:Reader,Writer
五、IO流体系图-常用的类
六、FileInputStream常用方法
学习任务:请使用 FileInputStream 读取 hello.txt 文件,并将文件内容显示
先在e盘下创建hello.txt输入内容hello world
package com.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
//字节流文件的输入程序
public class FileInputStream_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath="e:\\hello.txt";
int readData=0;
FileInputStream fileInputStream=null;
try {
//创建 FileInputStream 对象,用于读取文件
fileInputStream=new FileInputStream(filePath);
//从该输入流读取一个字节的数据。 如果没有输入可用,此方法将阻止。
//如果返回-1 , 表示读取完毕
while ((readData = fileInputStream.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)readData);//转成 char 显示
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
//关闭文件流
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}七、FileOutputStream常用方法
学习任务:请使用 FileOutputStream 在 abc.txt 文件,中写入 “hello,world”. 如果文件不存在,会创建 文件(注意:前提是目录已经存在.)
package com.hspedu.outputstream_;
import java.io.*;
public class FileOutputStream01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = "D:\\abc.txt";
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
//得到 FileOutputStream 对象 对象
//1. new FileOutputStream(filePath) 创建方式,当写入内容是,会覆盖原来的内容
// 2. new FileOutputStream(filePath, true) 创建方式,当写入内容是,是追加到文件后面
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath);
//写入一个字节
//fileOutputStream.write('H');
//写入字符串
String str = "hello,world!";
//str.getBytes() 可以把 字符串-> 字节数组
//fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes());
/*
write(byte[] b, int off, int len) 将 len 字节从位于偏移量 off 的指定字节数组写入此文件输出流
*/
fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes(), 0, 3);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}学习任务:编程完成图片/音乐 的拷贝
package com.hspedu.outputstream_;
import java.io.*;
public class FileCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String srcFilePath="e:\\9030.jpg";
String destFilePath="e:\\9031.jpg";
FileInputStream fileInputStream=null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream=null;
try {
fileInputStream=new FileInputStream(srcFilePath);
fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream(destFilePath);
//定义一个字节数组,提高读取效果
byte[] buf=new byte[1024];
int readLen=0;
while ((readLen=fileInputStream.read(buf))!=-1){
fileOutputStream.write(buf,0,readLen);
}
System.out.println("拷贝成功!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try{
if(fileInputStream!=null){
fileInputStream.close();
}
if(fileOutputStream!=null){
fileInputStream.close();
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}八、FileReader常用方法
- new FileReader(File/String)
- read:每次读取单个字符,返回该字符,如果到文件末尾返回-1
- read(char[]):批量读取多个字符到数组,返回读取到的字符数,如果到文件末尾返回-1
- 相关API:
- new String(char[]):将char[]转换成String
- new String(char[],off,len):将char[]的指定部分转换成String
九、FileWriter常用方法
- new FileWriter(File/String):覆盖模式,相当于流的指针在首端
- new FileWriter(File/String,true):追加模式,相当于流的指针在尾端
- write(int):写入单个字符
- write(char[]):写入指定数组
- write(char[],off,len):写入指定数组的指定部分
- write(string):写入单个字符
- write(string[],off,len):写入字符串的指定部分
- 相关API:String类:toCharArray:将String转换成char[]
- FileWriter使用后,必须要关闭(close)或刷新(flush), 否则写入不到指定的文件!
学习任务:使用 FileReader 从 story.txt ,这一步先在story.txt存在数据,然后在端口输出数据显示出来
package com.reader_;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ReadFile01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath="e:\\story.txt";
FileReader fileReader=null;
int data=0;
//创建FileReader对象
try{
fileReader =new FileReader(filePath);
//循环读取 使用 read, 单个字符读取
while((data=fileReader.read())!=-1){
//data数值为整数型,强制转换为字符
System.out.print((char)data);
}
}catch(
IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try{
if(fileReader!=null){
//关闭文件流
fileReader.close();
}
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}学习任务:字符数组读取文件
package com.reader_;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ReadFile02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath="e:\\story.txt";
FileReader fileReader=null;
int readLen=0;
char[] buf=new char[8];
//创建FileReader对象
try{
fileReader =new FileReader(filePath);
//循环读取 使用 read(buf), 返回的是实际读取到的字符数
//如果返回-1, 说明到文件结束
while((readLen=fileReader.read(buf))!=-1){
System.out.print(new String(buf,0,readLen));
}
}catch(
IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try{
if(fileReader!=null){
fileReader.close();
}
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}学习任务:使用 FileWriter 将 “风雨之后,定见彩虹” 写入到 note.txt 文件中
package com.hspedu.writer_;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileWriter_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath="e:\\noth.txt";
FileWriter fileWriter=null;
char[] chars={'a','b','c'};
try {
fileWriter = new FileWriter(filePath);
//3) write(int):写入单个字符
fileWriter.write('H');
// 4) write(char[]):写入指定数组
fileWriter.write(chars);
// 5) write(char[],off,len):写入指定数组的指定部分
fileWriter.write("程序员飞鸟".toCharArray(), 0, 3);
// 6) write(string):写入整个字符串
fileWriter.write(" 你好广州");
fileWriter.write("风雨之后,定见彩虹");
// 7) write(string,off,len):写入字符串的指定部分
fileWriter.write("上海天津", 0, 2);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
//对应 FileWriter , 一定要关闭流,或者 flush 才能真正的把数据写入文件里面
fileWriter.flush();//关闭文件流
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("程序结束~");
}
}到此这篇关于Java细数IO流基础到方法使用的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java IO流内容请搜索Devmax以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持Devmax!