配置文件的读取顺序
- 根目录/config/application.properties
- 根目录/config/application.yml
- 根目录/application.properties
- 根目录/application.yml
- classpath目录/config/application.properties
- classpath目录/config/application.yml
- classpath目录/application.properties
- classpath目录/application.yml
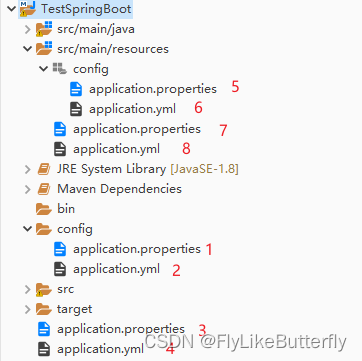
默认可读取的配置文件全部都会被读取合并,按照顺序读取配置,相同的配置项按第一次读取的值为准,同一个目录下properties文件比yml优先读取,通常会把配置文件放到classpath下,一般是resources里;
多坏境的配置文件
通常可以使用4个配置文件:(yml也同理)
- application.properties:默认配置文件
- application-dev.properties:开发环境配置文件
- application-prod.properties:生产环境配置文件
- application-test.properties:测试环境配置文件
在application.properties里配置spring.profiles.active以指定使用哪个配置文件,可以配置dev、prod、test分别对应以-dev、-prod、-test结尾的配置文件;(yml配置文件也是同理)
也可以在命令行使用spring.profiles.active指定,例如:java -jarxxxxxx.jar--spring.profiles.active=dev;
个性化配置
对于更特殊的个性化配置可以使用@Profile注解指定;
@Profile标签可以用在@Component或者@Configuration修饰的类上,可以标记类和方法,用来指定配置名字,然后使用spring.profiles.active指定该配置名字就可生效;
就像这样:
package testspringboot.test2;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile;
@Configuration
@Profile("myconfig")
public class MyConfig {
@Bean("Tom")
@Profile("A")
public String a() {
return "tomtom";
}
@Bean("Tom")
@Profile("B")
public String b() {
return "TOMTOM";
}
@Bean("Tom")
public String c() {
return "ttoomm";
}
}然后写一个controller类:
package testspringboot.test2;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test2controller")
public class Test2Controller {
@Resource(name = "Tom")
public String t;
@RequestMapping("/test2")
public String test2() {
System.out.println(t);
return "TEST2" t;
}
}启动类:
package testspringboot.test2;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Test2Main {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Test2Main.class, args);
}
}配置文件里配置:
server.port=8888
server.servlet.context-path=/testspringboot
spring.profiles.active=myconfig
只指定myconfig配置,则MyConfig类里c()的bean生效,访问结果是:
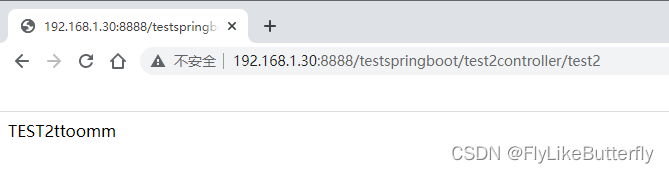
修改spring.profiles.active=myconfig,A,则MyConfig类里标记@Profile("A")的bean生效:
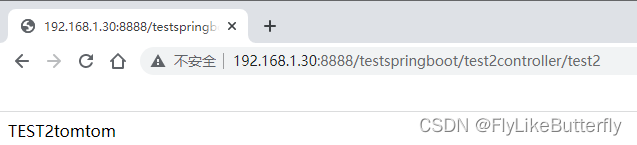
修改spring.profiles.active=myconfig,B,则标记@Profile("B")的bean生效:
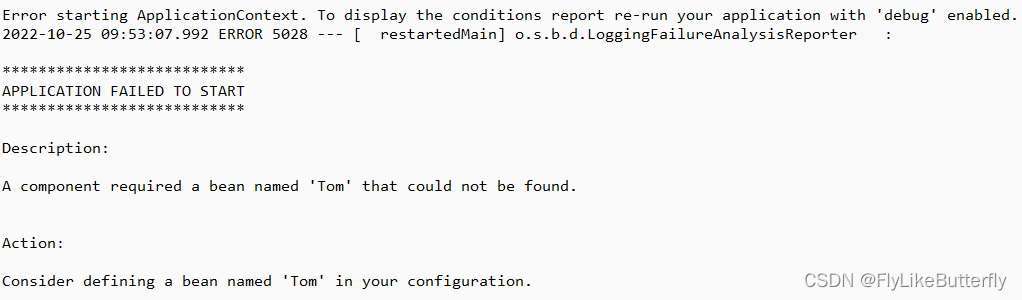
如果去掉spring.profiles.active配置,则就找不到MyConfig里的配置了,启动失败:
自定义配置文件名称和路径
可以使用@PropertySource标签指定自定义的配置文件名称和路径;(默认能加载到的配置文件也会先被加载)
通常只会用到设置配置文件的名字,并且配置文件的名字可以随便定义,可以叫xxxx.properties、a.txt、b.abc等等,但是内容格式需要跟.properties一致,即kv格式,所以不能直接加载yml格式的配置文件;
@PropertySource默认加载路径是classpath下,可以使用classpath:xxxx/xxxx/xxxx.properties指定目录和文件,如果使用根目录则需要使用file:xxxx/xxxx/xxxx.properties;
可以使用@PropertySource为启动类指定springboot的配置文件,能够做到使用一个main方法启动两个springboot实例,并各自使用不同的配置文件:
@SpringBootApplication
@PropertySource("classpath:a.properties")
@PropertySource(value = "file:a.properties", ignoreResourceNotFound = true)
public class Test2Main {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Test2Main.class, args);
}
}也可以使用@PropertySource配置bean,在使用@Component和@ConfigurationProperties时也可给bean指定特定配置文件:
放在resources下的配置文件tom.abc:
mybean.name=Tom
mybean.age=12
bean类ABC,配置tom.abc文件注入:
package testspringboot.test2;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties("mybean")
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:tom.abc")
public class ABC {
public String name;
public int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ABC [name=" name ", age=" age "]";
}
}启动类可以直接获得bean:
package testspringboot.test2;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
@SpringBootApplication
@PropertySource("classpath:a.properties")
@PropertySource(value = "file:a.properties", ignoreResourceNotFound = true)
public class Test2Main {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext ctx = SpringApplication.run(Test2Main.class, args);
System.out.println(ctx.getBean(ABC.class));
}
}启动结果:

可以直接获得配置的bean,也可以在代码里使用@Resource或者@Autowired获得;
加载yml文件
如果使用@PropertySource配置yml,则需要自定义一个factory实现:
package testspringboot.test2;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.YamlPropertiesFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.core.env.PropertiesPropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.EncodedResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PropertySourceFactory;
public class YmlPropertiesFactory implements PropertySourceFactory {
@Override
public PropertySource<?> createPropertySource(String name, EncodedResource resource) throws IOException {
YamlPropertiesFactoryBean factoryBean = new YamlPropertiesFactoryBean();
factoryBean.setResources(resource.getResource());
factoryBean.afterPropertiesSet();
Properties source = factoryBean.getObject();
return new PropertiesPropertySource("myyml", source);
}
}然后在@PropertySource里配置factory和yml文件:@PropertySource(value = "myapplication.yml", factory = YmlPropertiesFactory.class),就可以加载yml配置文件了;
到此这篇关于SpringBoot配置文件加载方法详细讲解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringBoot配置文件内容请搜索Devmax以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持Devmax!