MVVM和MVVMLight框架介绍及在项目中的使用详解
上一篇我们已经介绍了如何使用NuGet把MVVMLight应用到我们的WPF项目中。这篇我们来了解下一个基本的MVVMLight框架所必须的结构和运行模式。
MVVMLight安装之后,我们可以看到简易的框架布局,如上篇,生成了一个ViewModel文件夹,ViewModel层的内容都放在这边,除了Main对象的ViewModel之外,还包含一个ViewModelLocator文件,
用来注入当前的ViewModel全局实例。
一、先来说说分层结构:
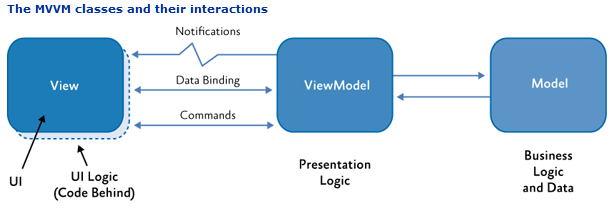
如图:
1、View负责前端展示,与ViewModel进行数据和命令的交互。
2、ViewModel,负责前端视图业务级别的逻辑结构组织,并将其反馈给前端。
3、Model,主要负责数据实体的结构处理,与ViewModel进行交互。
根据上述的分层,我们来进行编码。
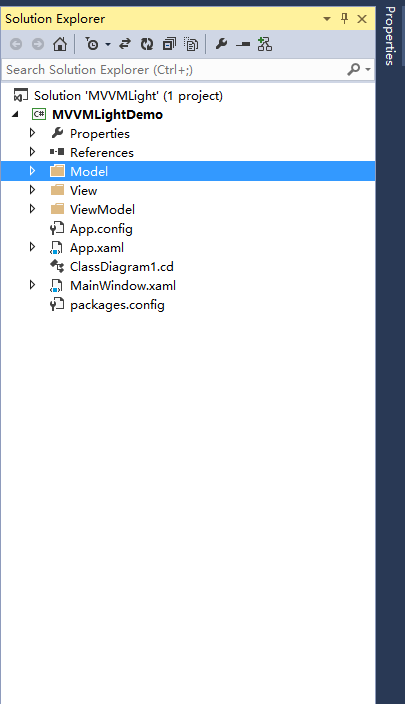
先建立一个完整三层结构的目录,如图,包含Model、View、ViewModel三层文件夹:
1、写一个Model,代码如下:
using GalaSoft.MvvmLight;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MVVMLightDemo.Model
{
public class WelcomeModel : ObservableObject
{
private String introduction;
/// <summary>
/// 欢迎词
/// </summary>
public String Introduction
{
get { return introduction; }
set { introduction = value; RaisePropertyChanged(()=>Introduction); }
}
}
很简单,仅仅是包含一个实体对象,这边注意的的是那他继承了一个父类:ObservableObject,这个父类的作用就是保证能够检测属性是否被改变。
它实现了INotifyPropertyChanged接口,通过触发PropertyChanged事件达到通知UI更改的目的;
所以我们在定义实体对象的时候,只需要调用RaisePropertyChanged(PropertyName)就可以进行属性更改通知了。
所以实体里面定义的每个属性都加上RaisePropertyChanged(PropertyName)的调用,就可以实现对UI的交互更新了。
2、写一个VideModel,来负责跟View的交互。
using GalaSoft.MvvmLight;
using MVVMLightDemo.Model;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MVVMLightDemo.ViewModel
{
public class WelcomeViewModel:ViewModelBase
{
/// <summary>
/// 构造函数
/// </summary>
public WelcomeViewModel()
{
Welcome = new WelcomeModel() { Introduction = "Hello World!" };
}
#region 属性
private WelcomeModel welcome;
/// <summary>
/// 欢迎词属性
/// </summary>
public WelcomeModel Welcome
{
get { return welcome; }
set { welcome = value; RaisePropertyChanged(()=>Welcome); }
}
#endregion
}
}也很简单,包含了一个命名为Welcome的WelcomeModel属性,继承了ViewBaseModel父类,
ViewBaseModel同时继承 ObservableObject类和ICleanup接口。所以他同样有INotifyPropertyChanged接口的能力,
能够通过触发PropertyChanged事件达到通知View的目的;
构造函数中对 Welcome 属性进行了实例化。
3、写一个View,来显示和交互ViewModel。
<Window x:Class="MVVMLightDemo.View.WelcomeView"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="WelcomeView" Height="300" Width="300">
<Grid>
<StackPanel VerticalAlignment="Center" HorizontalAlignment="Center" >
<TextBlock Text="{Binding Welcome.Introduction}" FontSize="30" ></TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
</Grid>
</Window>TextBlock 绑定了 Welcome.Introduction,所以应该显示Welcome对象下的Introduction属性。
这时候的ViewModel和View是没有任何关系的,所以我们在code-Behind的构造函数中写上如下代码:
using MVVMLightDemo.ViewModel;
using System.Windows;
namespace MVVMLightDemo.View
{
/// <summary>
/// Interaction logic for WelcomeView.xaml
/// </summary>
public partial class WelcomeView : Window
{
public WelcomeView()
{
InitializeComponent();
this.DataContext = new WelcomeViewModel();
}
}
把 WelcomeViewModel 赋值给当前视图的数据上下文。所以可以在当前视图中使用ViewModel中所有的公开属性和命令。
执行效果如下:
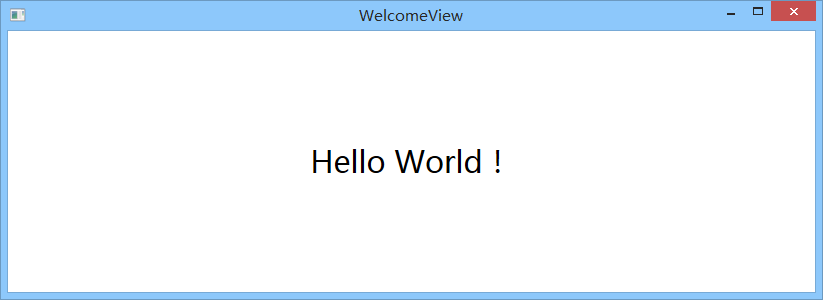
二、再来说说构造器:
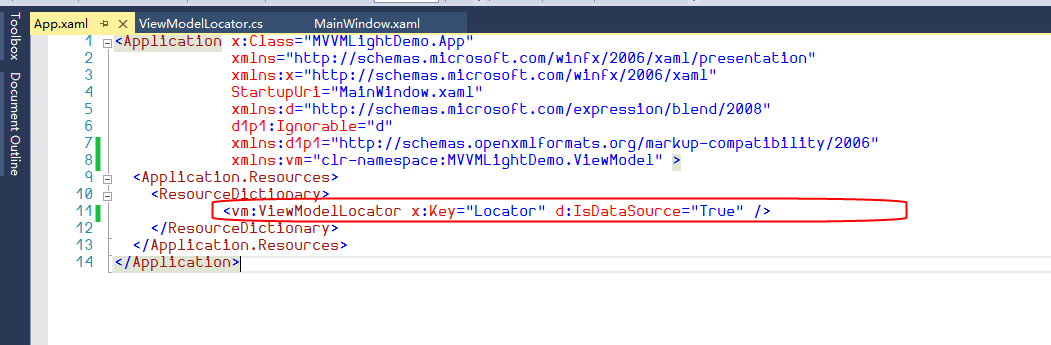
如果使用NuGet安装的是完整的一个是MVVM Light 框架,而非 MVVM Light libraries only的时候,总是会带上ViewModelLocator类,并且生成资源字典并加入到了全局资源中。
<Application x:Class="MVVMLightDemo.App"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
StartupUri="View/WelcomeView.xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
d1p1:Ignorable="d"
xmlns:d1p1="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:vm="clr-namespace:MVVMLightDemo.ViewModel" >
<Application.Resources>
<ResourceDictionary>
<vm:ViewModelLocator x:Key="Locator" d:IsDataSource="True" />
</ResourceDictionary>
</Application.Resources>
</Application>所以每次App初始化的时候,就会去初始化ViewModelLocator类。
实际上他就是一个很基本的视图模型注入器。在构造器中把使用到的ViewModel统一注册,并生成单一实例。
然后使用属性把它暴露出来,每当我们访问属性的时候,就会返回相应的ViewModel实例。
/*
In App.xaml:
<Application.Resources>
<vm:ViewModelLocator xmlns:vm="clr-namespace:MVVMLightDemo"
x:Key="Locator" />
</Application.Resources>
In the View:
DataContext="{Binding Source={StaticResource Locator}, Path=ViewModelName}"
You can also use Blend to do all this with the tool's support.
See http://www.galasoft.ch/mvvm
*/
using GalaSoft.MvvmLight;
using GalaSoft.MvvmLight.Ioc;
using Microsoft.Practices.ServiceLocation;
namespace MVVMLightDemo.ViewModel
{
/// <summary>
/// This class contains static references to all the view models in the
/// application and provides an entry point for the bindings.
/// </summary>
public class ViewModelLocator
{
/// <summary>
/// Initializes a new instance of the ViewModelLocator class.
/// </summary>
public ViewModelLocator()
{
ServiceLocator.SetLocatorProvider(() => SimpleIoc.Default);
#region Code Example
////if (ViewModelBase.IsInDesignModeStatic)
////{
//// // Create design time view services and models
//// SimpleIoc.Default.Register<IDataService, DesignDataService>();
////}
////else
////{
//// // Create run time view services and models
//// SimpleIoc.Default.Register<IDataService, DataService>();
////}
#endregion
SimpleIoc.Default.Register<MainViewModel>();
}
#region 实例化
public MainViewModel Main
{
get
{
return ServiceLocator.Current.GetInstance<MainViewModel>();
}
}
#endregion
public static void Cleanup()
{
// TODO Clear the ViewModels
}
}
注意的是,这边把MVVMLight 自带的SimpleIoc作为默认的服务提供者,它是个简易的注入框架。
为了统一化,并且在设计的时候可以看到看到ViewModel的数据,这边用ServiceLocator 又将SimpleIoc包裹了一层。
上面我们写了一个Hello World,这时候就可以用这种方式改装了。
/*
In App.xaml:
<Application.Resources>
<vm:ViewModelLocator xmlns:vm="clr-namespace:MVVMLightDemo"
x:Key="Locator" />
</Application.Resources>
In the View:
DataContext="{Binding Source={StaticResource Locator}, Path=ViewModelName}"
You can also use Blend to do all this with the tool's support.
See http://www.galasoft.ch/mvvm
*/
using GalaSoft.MvvmLight;
using GalaSoft.MvvmLight.Ioc;
using Microsoft.Practices.ServiceLocation;
namespace MVVMLightDemo.ViewModel
{
/// <summary>
/// This class contains static references to all the view models in the
/// application and provides an entry point for the bindings.
/// </summary>
public class ViewModelLocator
{
/// <summary>
/// Initializes a new instance of the ViewModelLocator class.
/// </summary>
public ViewModelLocator()
{
ServiceLocator.SetLocatorProvider(() => SimpleIoc.Default);
#region Code Example
////if (ViewModelBase.IsInDesignModeStatic)
////{
//// // Create design time view services and models
//// SimpleIoc.Default.Register<IDataService, DesignDataService>();
////}
////else
////{
//// // Create run time view services and models
//// SimpleIoc.Default.Register<IDataService, DataService>();
////}
#endregion
SimpleIoc.Default.Register<MainViewModel>();
SimpleIoc.Default.Register<WelcomeViewModel>();
}
#region 实例化
public MainViewModel Main
{
get
{
return ServiceLocator.Current.GetInstance<MainViewModel>();
}
}
public WelcomeViewModel Welcome
{
get
{
return ServiceLocator.Current.GetInstance<WelcomeViewModel>();
}
}
#endregion
public static void Cleanup()
{
// TODO Clear the ViewModels
}
}
注册完WelcomeViewModel实例之后,我们就可以在相应的View中使用了 ,原本的
public WelcomeView()
{
InitializeComponent();
this.DataContext = new WelcomeViewModel();
}中的 this.DataContext = new WelcomeViewModel();
可以去掉了,直接在WelcomeView中这样写:
DataContext="{Binding Source={StaticResource Locator},Path=Welcome}"
如下图:
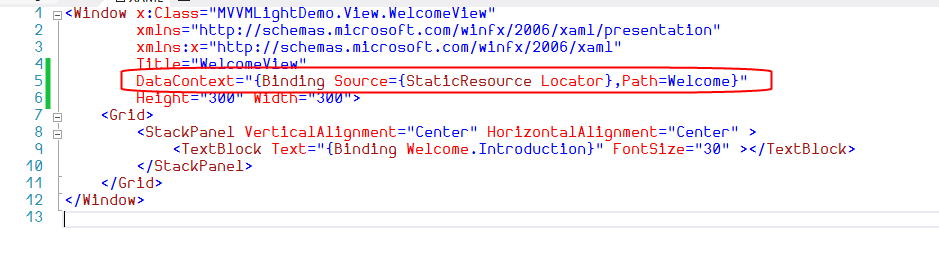
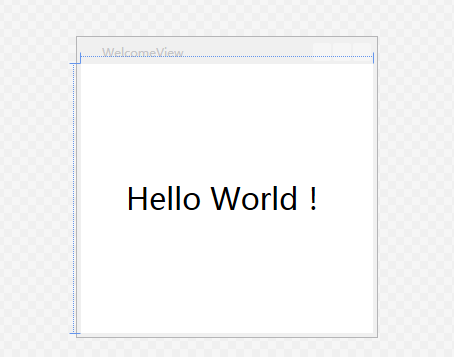
这样做的好处,一个是绑定化相对于简单粗暴的赋值方式,更合理。一个是在可视化窗口可以看到所绑定的数据,达到所见即所得的友好效果。
如下:
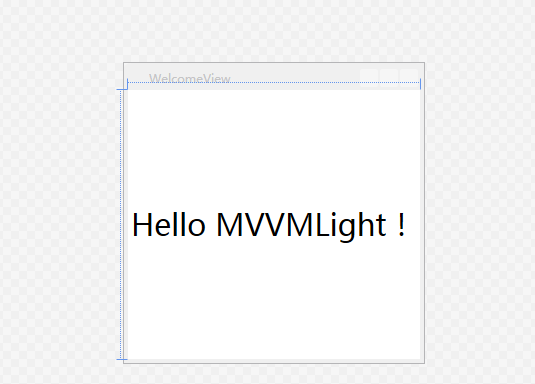
当我们改掉绑定到的数据,编译之后就会立马呈现:
服务端开发人员可以专心写ViewModel的业务逻辑代码,UI开发人员可以专注设计视图了,
同样 ViewModel可以绑定到不同的视图上,所以从这边就可以体现出他其中的三个重要特性:低耦合、可重用性、独立开发。
大家有没有发现ViewModelLocator 类中还有个 ClearnUp()方法,主要目的用来清除ViewModel实例的。
ViewModelBase继承了GalaSoft.MvvmLight.ICleanup接口,并在自己的类中写好了Cleanup()虚方法。所以我们在实例ViewModel类中可以重写Cleanup()来达到清除当前实例的目的。
以上就是MVVMLight 之Model View结构及全局视图模型注入器的详细内容,更多关于ViewModel 结构及全局视图模型注入器的资料请关注Devmax其它相关文章!