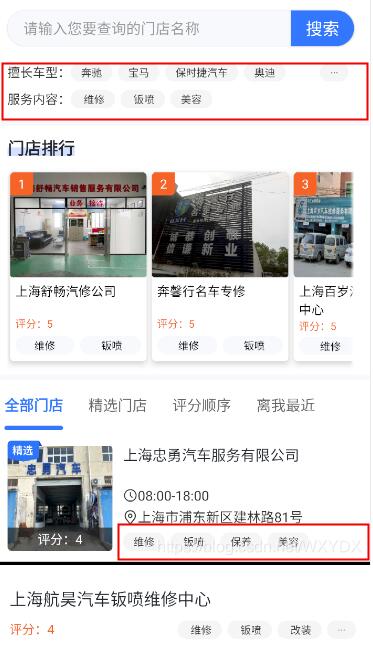
近期产品提了有关流式布局的新需求,要求显示字数不定的标签,如果一行显示不完,就只显示一行的内容,而且还在一两个页面采取了多种样式,无语了
自己归类了一下,需求有以下几个区别
1:可选择添加标签与否
2:是否有具体数量限制(比如最多显示3个)
3:是否要靠右对齐
有需求,先找一波现有的工具,看是不是可以直接用
参考Android流式布局实现热门标签效果
FlowLayout原样式:

这个和我们的需求已经比较符合了,但是他并不能控制只显示单行内容
如果要实现这样的布局,官方也提供了Flexbox和FlexboxLayout,但查阅文档后发现他们都不支持设置单行,如果强行设置maxlines为1,所有子view都会被减少宽度来让第一行挤下所有的子view
希望的样式(第一行内能放下多少就放多少,第二行开始都不显示,也不占用高度):
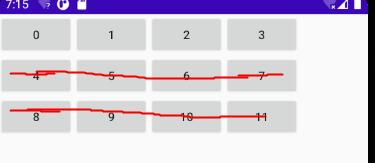
实际上:

可以看到这些view的宽度都被严重压缩了,即使设置了padding也是没有用的。正好项目本身使用了FlowLayout,就在他的基础上进行修改。
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Build;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import androidx.annotation.RequiresApi;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class SingleLineFlowLayout extends ViewGroup {
private static final String TAG = "FlowLayout";
public int position=-1;
public boolean alignRight;
public boolean countMore;
private List<List<View>> mLineViews = new ArrayList<List<View>>();
private List<Integer> mLineHeight = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public SingleLineFlowLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public SingleLineFlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public SingleLineFlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@RequiresApi(api = Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP)
public SingleLineFlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
}
/**
* 测量所有子View大小,确定ViewGroup的宽高
*
* @param widthMeasureSpec
* @param heightMeasureSpec
*/
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//由于onMeasure会执行多次,避免重复的计算控件个数和高度,这里需要进行清空操作
mLineViews.clear();
mLineHeight.clear();
//获取测量的模式和尺寸大小
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec) - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight();
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec) getPaddingTop() getPaddingBottom();
//记录ViewGroup真实的测量宽高
int viewGroupWidth = widthSize;
int viewGroupHeight = getPaddingTop() getPaddingBottom();
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY && heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
viewGroupWidth = widthSize;
viewGroupHeight = heightSize;
} else {
//当前所占的宽高
int currentLineWidth = 0;
int currentLineHeight = 0;
int lastChildWidth=0;
int doubleLastChildWidth=0;
//用来存储每一行上的子View
List<View> lineView = new ArrayList<View>();
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i ) {
View childView = getChildAt(i);
//对子View进行测量
measureChild(childView, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
MarginLayoutParams marginLayoutParams = (MarginLayoutParams) childView.getLayoutParams();
int childViewWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth() marginLayoutParams.leftMargin marginLayoutParams.rightMargin;
int childViewHeight = childView.getMeasuredHeight() marginLayoutParams.topMargin marginLayoutParams.bottomMargin;
if (currentLineWidth childViewWidth > widthSize) {
//从当前位置开始,删除view,保留最后一个moreView
String tag=(String) childView.getTag();
if (tag!=null&&tag.equals("More")){
currentLineHeight = Math.max(currentLineHeight, childViewHeight);
}else {
removeViews(i,getChildCount()-1-i);
childView = getChildAt(i);
tag=(String) childView.getTag();
if (tag==null||!tag.equals("More")){
currentLineHeight = Math.max(currentLineHeight, childViewHeight);
}else {
//对子View进行测量
measureChild(childView, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
marginLayoutParams = (MarginLayoutParams) childView.getLayoutParams();
childViewWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth() marginLayoutParams.leftMargin marginLayoutParams.rightMargin;
childViewHeight = childView.getMeasuredHeight() marginLayoutParams.topMargin marginLayoutParams.bottomMargin;
if (currentLineWidth childViewWidth > widthSize) {
//lineView.remove(i-1);
lineView.remove(getChildAt(i-1));
removeViewAt(i-1);
currentLineWidth=currentLineWidth-lastChildWidth;
}
if (i-1>0&¤tLineWidth childViewWidth > widthSize){
currentLineWidth=currentLineWidth-doubleLastChildWidth-marginLayoutParams.leftMargin - marginLayoutParams.rightMargin;
lineView.remove(getChildAt(i-2));
removeViewAt(i-2);
}
currentLineWidth = childViewWidth;
currentLineHeight = Math.max(currentLineHeight, childViewHeight);
//添加行对象里的子View
if (alignRight){
int rightMargin=marginLayoutParams.rightMargin;
marginLayoutParams.setMargins(marginLayoutParams.leftMargin,marginLayoutParams.topMargin,0,marginLayoutParams.bottomMargin);
childView.setLayoutParams(marginLayoutParams);
marginLayoutParams=(MarginLayoutParams) getChildAt(0).getLayoutParams();
marginLayoutParams.setMargins(marginLayoutParams.leftMargin widthSize-currentLineWidth rightMargin,marginLayoutParams.topMargin,marginLayoutParams.rightMargin,marginLayoutParams.bottomMargin);
getChildAt(0).setLayoutParams(marginLayoutParams);
}else {
marginLayoutParams.setMargins(widthSize-currentLineWidth,marginLayoutParams.topMargin,0,marginLayoutParams.bottomMargin);
childView.setLayoutParams(marginLayoutParams);
}
lineView.add(childView);
}
}
} else {
//当前行宽 子View 左右外边距<=ViewGroup的宽度,不换行
if (i>1){
doubleLastChildWidth=lastChildWidth;
}
lastChildWidth=childViewWidth;
currentLineWidth = childViewWidth;
currentLineHeight = Math.max(currentLineHeight, childViewHeight);
//添加行对象里的子View
String tag=(String) childView.getTag();
if (tag!=null&&tag.equals("More")){
if (countMore){
lineView.add(childView);
}
}else {
lineView.add(childView);
}
}
if (i >= getChildCount() - 1) {
//最后一个子View的时候
//添加行对象
if (alignRight){
int rightMargin=marginLayoutParams.rightMargin;
marginLayoutParams.setMargins(marginLayoutParams.leftMargin,marginLayoutParams.topMargin,0,marginLayoutParams.bottomMargin);
childView.setLayoutParams(marginLayoutParams);
marginLayoutParams=(MarginLayoutParams) getChildAt(0).getLayoutParams();
marginLayoutParams.setMargins(marginLayoutParams.leftMargin widthSize-currentLineWidth rightMargin,marginLayoutParams.topMargin,marginLayoutParams.rightMargin,marginLayoutParams.bottomMargin);
getChildAt(0).setLayoutParams(marginLayoutParams);
}
mLineViews.add(lineView);
viewGroupWidth = Math.max(childViewWidth, widthSize);
viewGroupHeight = viewGroupHeight currentLineHeight;
//添加行高
mLineHeight.add(currentLineHeight);
}
}
}
setMeasuredDimension(viewGroupWidth, viewGroupHeight);
}
/**
* 设置ViewGroup里子View的具体位置
*
* @param changed
* @param l
* @param t
* @param r
* @param b
*/
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int left = getPaddingLeft();
int top = getPaddingTop();
//一共有几行
int lines = mLineViews.size();
for (int i = 0; i < lines; i ) {
//每行行高
int lineHeight = mLineHeight.get(i);
//行内有几个子View
List<View> viewList = mLineViews.get(i);
int views = viewList.size();
for (int j = 0; j < views; j ) {
View view = viewList.get(j);
MarginLayoutParams marginLayoutParams = (MarginLayoutParams) view.getLayoutParams();
int vl = left (j == 0 ? 0 : marginLayoutParams.leftMargin);
if (alignRight){
vl = left marginLayoutParams.leftMargin;
}
int vt = top marginLayoutParams.topMargin;
int vr = vl view.getMeasuredWidth();
int vb = vt view.getMeasuredHeight();
view.layout(vl, vt, vr, vb);
if (alignRight){
left = view.getMeasuredWidth() marginLayoutParams.leftMargin marginLayoutParams.rightMargin;
}else {
left = view.getMeasuredWidth() (j == 0 ? 0 : marginLayoutParams.leftMargin) marginLayoutParams.rightMargin;
}
}
left = getPaddingLeft();
top = lineHeight;
}
}
/**
* 指定ViewGroup的LayoutParams
*
* @param attrs
* @return
*/
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
}
使用方法:
1:使用addView()将所有的标签都添加到布局中
2:如果需要显示代表更多的标签,在添加完所有标签后,再添加对应的view,并且设置view.setTag("More")即可(该View会自动靠右对齐,并且会检测是否能放得下该标签,如果放不下的话会依次尝试两次从后往前删除子view后能否放得下,如果遇到特殊情况需要删除更多的子view的话,可以自己修改代码)
3:如果需要所有的view都右对齐,要在addView()前设置布局的alignRight=true
4:如果需要超过某个数量后,即使可以单行显示,也要添加更多标签的话,要在addView()前设置布局的countMore=true,使用addView()时自己控制添加的数量,并在超过数量的时候添加对应的view,并且设置view.setTag("More")
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持Devmax。