组合模式
组合模式(Composite Pattern)也称为整体-部分(Part-Whole)模式,属于结构型模式。
它的宗旨是通过将单个对象(叶子节点)和组合对象(树枝节点)用相同的接口进行表示,使得客户端对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性。
组合模式一般用来描述整体与部分的关系,它将对象组织到树形结构中,最顶层的节点称为根节点,根节点下面可以包含树枝节点和叶子节点,树枝节点下面又可以包含树枝节点和叶子节点。
应用场景
1.希望客户端可以忽略组合对象与单个对象的差异时。
2.对象层次具备整体和部分,呈树形结构。
例如:树形菜单,文件、文件夹的管理。
优缺点
优点:
1、高层模块调用简单。
2、节点自由增加。
缺点:
1.在使用组合模式时,其叶子和树枝的声明都是实现类,而不是接口,违反了依赖倒置原则。
主要角色
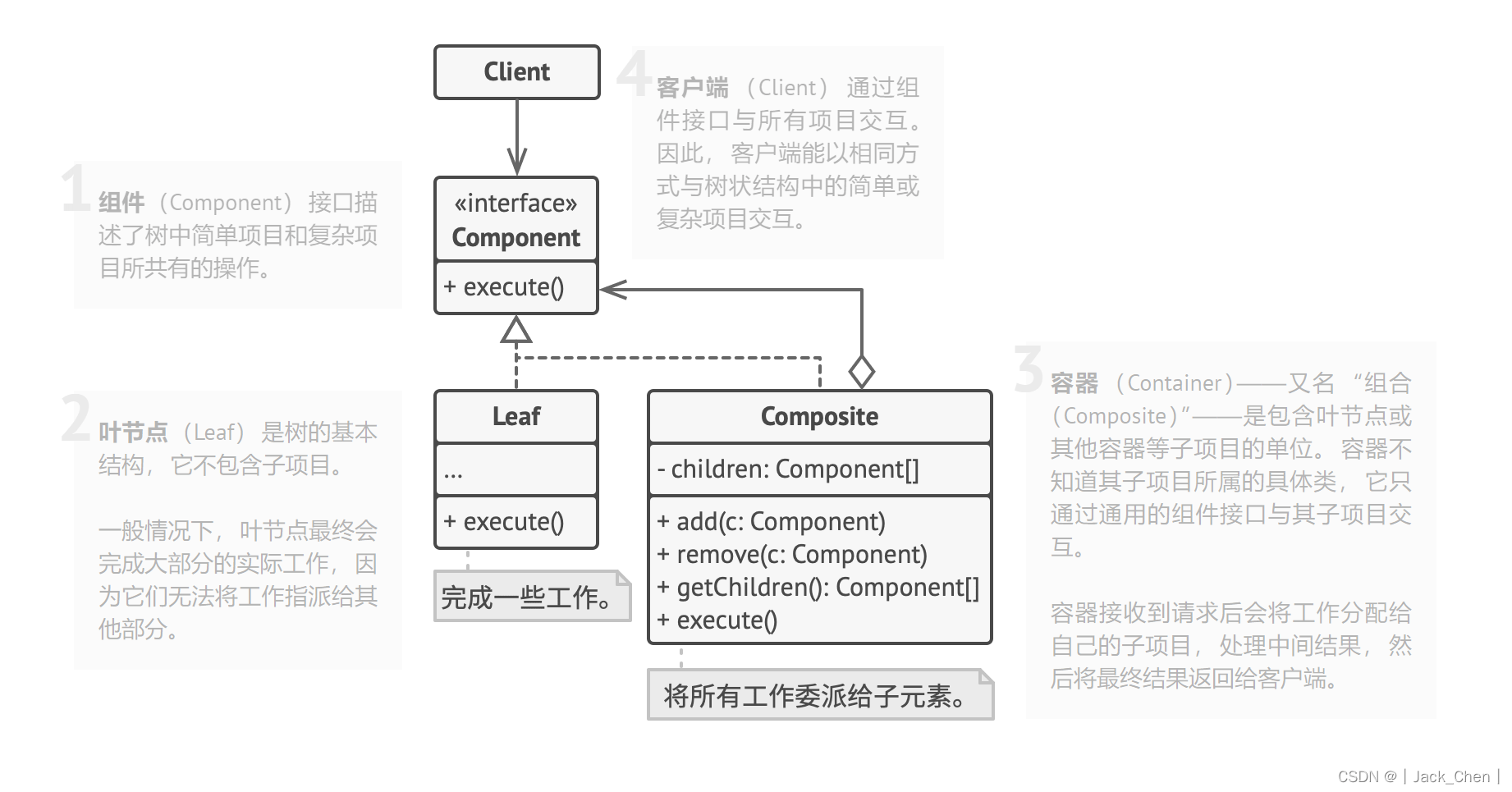
组合模式主要包含3个角色:
1.抽象根节点(Component)
定义系统各层次对象的共有方法和属性,可以预先定义一些默认行为和属性。
2.树枝节点(Composite)
定义树枝节点的行为,存储子节点,组合树枝节点和叶子节点形成一个树形结构。
3.叶子节点(Laf)
叶子节点对象,其下再无分支,是系统层次遍历的最小单位。
组合模式结构
分类
组合模式在具体实现上,有两种不同的方式,分别是透明组合模式和安全组合模式。
透明组合模式将公共接口封装到抽象根节点(Component)中,系统所有节点具备一致行为,如果当系统绝大多数层次具备相同的公共行为时,采用透明组合模式会更好。但是为剩下少数层次节点引入不需要的方法。
如果当系统各个层次差异性行为较多或者树节点层次相对稳定时,则采用安全组合模式。
透明组合模式
透明组合模式是把所有公共方法都定义在抽象根节点中,这样做的好处是客户端无需分辨是叶子节点(Leaf)和树枝节点(Composite),它们具备完全一致的接口。缺点是叶子节点(Leaf)会继承得到一些它所不需要(管理子类操作的方法)的方法,这与设计模式接口隔离原则相违背。
创建抽象根节点
把所有可能用到的方法都定义到这个最顶层的抽象类中,但是不写任何逻辑处理的代码,而是直接抛出异常。
禁止使用抽象方法,否则子类必须实现,于是体现不出各个子类的差异。子类只需要重写有差异的方法进行覆盖即可。
举例:分类目录为根节点,具体分类为树枝节点,分类下的商品为叶子节点。
public abstract class Component {
public String getName(Component component) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("getName is not supported");
}
public double getPrice(Component component) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("getPrice is not supported");
}
public String print() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("print is not supported");
}
public boolean addChild(Component component) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("addChild is not supported");
}
public boolean removeChild(Component component) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("removeChild is not supported");
}
public Component getChild(int index) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("getChild is not supported");
}
}创建树枝节点
public class CompositeCategory extends Component {
private String name;
private List<Component> componentList = new ArrayList<Component>();
public CompositeCategory(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String print() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(this.name);
for (Component component : this.componentList) {
if (component instanceof CompositeCategory) {
builder.append("\n" " -" component.print());
} else {
builder.append("\n" " --" component.print());
}
}
return builder.toString();
}
@Override
public boolean addChild(Component component) {
return this.componentList.add(component);
}
@Override
public boolean removeChild(Component component) {
return this.componentList.remove(component);
}
@Override
public Component getChild(int index) {
return this.componentList.get(index);
}
}创建叶子节点
public class CompositeProduct extends Component {
private String name;
private Double price;
public CompositeProduct(String name, Double price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String print() {
return this.name " (¥" this.price "元)";
}
@Override
public String getName(Component component) {
return this.name;
}
@Override
public double getPrice(Component component) {
return this.price;
}
}客户端调用
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 根节点
Component root = new CompositeCategory("分类目录");
// 树枝节点
Component categoryA = new CompositeCategory("分类A");
Component categoryB = new CompositeCategory("分类B");
// 叶子节点
Component productA = new CompositeProduct("productA ", 20.5);
Component productB = new CompositeProduct("productB ", 30.5);
Component productC = new CompositeProduct("productC", 25.5);
root.addChild(categoryA);
categoryA.addChild(productA);
root.addChild(categoryB);
categoryB.addChild(productB);
categoryB.addChild(productC);
System.out.println(root.print());
System.out.println("-----------------------");
Component child = root.getChild(1);
System.out.println(child.print());
System.out.println("-----------------------");
root.removeChild(categoryA);
System.out.println(root.print());
}
分类目录
-分类A
--productA (¥20.5元)
-分类B
--productB (¥30.5元)
--productC (¥25.5元)
-----------------------
分类B
--productB (¥30.5元)
--productC (¥25.5元)
-----------------------
分类目录
-分类B
--productB (¥30.5元)
--productC (¥25.5元)
安全组合模式
安全组合模式是只规定系统各个层次的最基础的一致行为,而把组合(树节点)本身的方法(管理子类对象的添加,删除等)放到自身当中。
安全组合模式的好处是接口定义职责清晰,符合设计模式单一职责原侧和接口隔离原则;缺点是客户需要区分树枝节点(Composite)和叶子节点(Leaf),这样才能正确处理各个层次的操作,客户端无法依赖抽象(Component),违背了设计模式依赖倒置原则。
创建抽象根节点
public abstract class Component {
protected String name;
public Component(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public abstract String print();
}
创建树枝节点
public class CompositeCategory extends Component {
private List<Component> componentList;
public CompositeCategory(String name) {
super(name);
this.componentList = new ArrayList<Component>();
}
@Override
public String print() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(this.name);
for (Component component : this.componentList) {
if (component instanceof CompositeCategory) {
builder.append("\n" " -" component.print());
} else {
builder.append("\n" " --" component.print());
}
}
return builder.toString();
}
public boolean addChild(Component component) {
return this.componentList.add(component);
}
public boolean removeChild(Component component) {
return this.componentList.remove(component);
}
public Component getChild(int index) {
return this.componentList.get(index);
}
}创建叶子节点
public class CompositeProduct extends Component {
private Double price;
public CompositeProduct(String name, Double price) {
super(name);
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String print() {
return this.name " (¥" this.price "元)";
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return this.price;
}
}客户端调用
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 根节点
CompositeCategory root = new CompositeCategory("分类目录");
// 树枝节点
CompositeCategory categoryA = new CompositeCategory("分类A");
CompositeCategory categoryB = new CompositeCategory("分类B");
// 叶子节点
CompositeProduct productA = new CompositeProduct("productA", 20.5);
CompositeProduct productB = new CompositeProduct("productB", 30.5);
CompositeProduct productC = new CompositeProduct("productC", 25.5);
root.addChild(categoryA);
categoryA.addChild(productA);
root.addChild(categoryB);
categoryB.addChild(productB);
categoryB.addChild(productC);
System.out.println(root.print());
System.out.println("-----------------------");
Component child = root.getChild(1);
System.out.println(child.print());
System.out.println("-----------------------");
root.removeChild(categoryA);
System.out.println(root.print());
}分类目录
-分类A
--productA (¥20.5元)
-分类B
--productB (¥30.5元)
--productC (¥25.5元)
-----------------------
分类B
--productB (¥30.5元)
--productC (¥25.5元)
-----------------------
分类目录
-分类B
--productB (¥30.5元)
--productC (¥25.5元)
到此这篇关于Java结构型设计模式之组合模式详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java组合模式内容请搜索Devmax以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持Devmax!