第三方库 binarytree
其使用环境、安装方法及二叉树的相关知识,请见:《Python 初识二叉树,新手也秒懂!》
不能导入的请安装:pip install binarytree
安装好了就导入库:import binarytree
主要的函数方法如下:
>>> import binarytree as bt >>> >>> bt.__all__ ['Node', 'tree', 'bst', 'heap', 'build', 'build2', 'get_parent', '__version__'] >>> >>> bt.__version__ '6.3.0' >>>
目前最新版本 V6.3.0,挑其中几个来探究一下二叉树的世界吧:
二叉树节点函数 Node()
函数原型:Node(NodeValue, LeftChildNode=None, LeftChildNode=None)
三个参数:NodeValue节点数值,必须为实数,int或float
LeftChildNode, LeftChildNode 左右子树节点
通过创建节点,生成一棵3层的满二叉树:
>>> from binarytree import Node
>>>
>>> bt = Node(1)
>>>
>>> bt.left = Node(2)
>>> bt.right = Node(3)
>>>
>>> bt.left.left = Node(4)
>>> bt.left.right = Node(5)
>>> bt.right.left = Node(6)
>>> bt.right.right = Node(7)
>>>
>>> bt.pprint()
__1__
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7
>>> 如果要建很多层的满二叉树,用Node()逐个赋值有点麻烦。比如到第四层要给8个叶子赋值:
>>> bt.left.left.left = Node(8)
>>> bt.left.right.left = Node(10)
>>> bt.right.left.left = Node(12)
>>> bt.right.right.left = Node(14)
>>> bt.left.left.right = Node(9)
>>> bt.left.right.right = Node(11)
>>> bt.right.left.right = Node(13)
>>> bt.right.right.right = Node(15)
每多一层叶子数就翻一倍,为了方便我想到用exec()函数把字符串转成变量操作赋值的方法予以简化代码。自定义函数 createPerfectTree(intTreeLevels, listTreeData),参数为需要指定的层数和节点赋值数据,分别是整数和列表类型;函数返回值为一个满二叉树。代码如下:
from binarytree import Node
def createPerfectTree(intTreeLevels, listTreeData):
if len(listTreeData) 1<2**intTreeLevels or intTreeLevels<1:
return None
t,tmp = ['root'],[]
data = listTreeData[::-1]
root = Node(data[-1])
data.pop()
for j in range(intTreeLevels-1):
for i in t:
exec(i f'.left=Node({data[-1]})')
data.pop()
exec(i f'.right=Node({data[-1]})')
data.pop()
tmp.append(i '.left')
tmp.append(i '.right')
t=tmp[:]
tmp=[]
return root
# 打印各节点值为整数序列的满二叉树(0~6层)
for i in range(7):
data = [*range(1,2**i)]
print(createPerfectTree(i, data))
# 用指定列表的数据,创建满二叉树
data = [15,0,7,2,6,4,3,1,5,6,7,9,34,23,8]
print(createPerfectTree(3, data))
print(createPerfectTree(4, data))
print(createPerfectTree(5, data)) # data长度不够返回:None
# 赋值后列印
root = createPerfectTree(4, [*range(1,2**4)])
print(root)运行结果:
None
1
1
/ \
2 3
__1__
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7
________1________
/ \
__2___ ___3___
/ \ / \
4 _5 _6 _7
/ \ / \ / \ / \
8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
____________________1____________________
/ \
________2_________ _________3_________
/ \ / \
___4___ ____5___ ____6___ ____7___
/ \ / \ / \ / \
_8 _9 _10 _11 _12 _13 _14 _15
/ \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \
16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
____________________________________________1____________________________________________
/ \
____________________2_____________________ _____________________3_____________________
/ \ / \
_________4_________ __________5_________ __________6_________ __________7_________
/ \ / \ / \ / \
____8___ ____9___ ____10___ ____11___ ____12___ ____13___ ____14___ ____15___
/ \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \
_16 _17 _18 _19 _20 _21 _22 _23 _24 _25 _26 _27 _28 _29 _30 _31
/ \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \
32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63
__15__
/ \
0 7
/ \ / \
2 6 4 3
______15_______
/ \
__0__ ___7___
/ \ / \
2 6 4 _3
/ \ / \ / \ / \
1 5 6 7 9 34 23 8
None
________1________
/ \
__2___ ___3___
/ \ / \
4 _5 _6 _7
/ \ / \ / \ / \
8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
嵌套创建节点,顺便判断对称性。得到一个结论:属性.is_symmetric判断的对称是指镜像对称,不是根节点的左右子树要完全相等,而是要镜面反向才返回 True。
>>> from binarytree import Node
>>> a=Node(1,Node(2,Node(3),Node(4)),Node(2,Node(3),Node(4)))
>>> a.pprint()
__1__
/ \
2 2
/ \ / \
3 4 3 4
>>> b=Node(1,Node(2,Node(3),Node(4)),Node(2,Node(4),Node(3)))
>>> b.pprint()
__1__
/ \
2 2
/ \ / \
3 4 4 3
>>> a.is_symmetric
False
>>> b.is_symmetric
True
>>> 二叉树的方法与属性
1. 列印方法bt.pprint() 等同于print(bt)
# 以下所有举例皆用上面代码中的 root 满二叉树:
>>> root
Node(1)
>>> root.pprint()
________1________
/ \
__2___ ___3___
/ \ / \
4 _5 _6 _7
/ \ / \ / \ / \
8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
# 等同于 print(root)
>>> root.right.pprint()
___3___
/ \
_6 _7
/ \ / \
12 13 14 15
>>> root.left.right.pprint()
_5
/ \
10 11
>>> print(root.left.left)
4
/ \
8 9
>>> 2. 判断类属性,判断二叉树是否平衡、严格、对称、完全、完美,是否为最大(小)堆、搜索树等
对称是指根节点的左右子树呈镜像对称;严格是指除叶子外所有节点都有左右两个节点。
>>> root.is_balanced True >>> root.is_bst False >>> root.is_complete True >>> root.is_max_heap False >>> root.is_min_heap True >>> root.is_perfect True >>> root.is_strict True >>> root.is_symmetric False >>>
3. 数量数值类属性
>>> root.left Node(2) >>> root.right Node(3) >>> root.val 1 >>> root.value 1 >>> root.values [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15] >>> root.values2 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15] >>> root.left.value 2 >>> root.right.left.value 6 >>> root.max_node_value 15 >>> root.min_node_value 1 >>> root.max_leaf_depth 3 >>> root.min_leaf_depth 3 >>> root.levels [[Node(1)], [Node(2), Node(3)], [Node(4), Node(5), Node(6), Node(7)], [Node(8), Node(9), Node(10), Node(11), Node(12), Node(13), Node(14), Node(15)]] >>> len(root.levels) # == height 1 4 >>> root.height 3 >>> root.leaves [Node(8), Node(9), Node(10), Node(11), Node(12), Node(13), Node(14), Node(15)] >>> len(root.leaves) 8 >>> root.leaf_count 8 >>>
注: val和value等价,values和values2差别在于如有多个连续空节点时后者只返回一个None
4. 属性字典,打包了上面两大类属性中的一部分放在一个字典里
>>> root.properties
{'height': 3,
'size': 15,
'is_max_heap': False,
'is_min_heap': True,
'is_perfect': True,
'is_strict': True,
'is_complete': True,
'leaf_count': 8,
'min_node_value': 1,
'max_node_value': 15,
'min_leaf_depth': 3,
'max_leaf_depth': 3,
'is_balanced': True,
'is_bst': False,
'is_symmetric': False
}5. 遍历类
>>> root.preorder [Node(1), Node(2), Node(4), Node(8), Node(9), Node(5), Node(10), Node(11), Node(3), Node(6), Node(12), Node(13), Node(7), Node(14), Node(15)] >>> root.inorder [Node(8), Node(4), Node(9), Node(2), Node(10), Node(5), Node(11), Node(1), Node(12), Node(6), Node(13), Node(3), Node(14), Node(7), Node(15)] >>> root.postorder [Node(8), Node(9), Node(4), Node(10), Node(11), Node(5), Node(2), Node(12), Node(13), Node(6), Node(14), Node(15), Node(7), Node(3), Node(1)] >>> root.levelorder [Node(1), Node(2), Node(3), Node(4), Node(5), Node(6), Node(7), Node(8), Node(9), Node(10), Node(11), Node(12), Node(13), Node(14), Node(15)] >>> >>> root.left.levelorder [Node(2), Node(4), Node(5), Node(8), Node(9), Node(10), Node(11)] >>> root.right.left.preorder [Node(6), Node(12), Node(13)] >>>
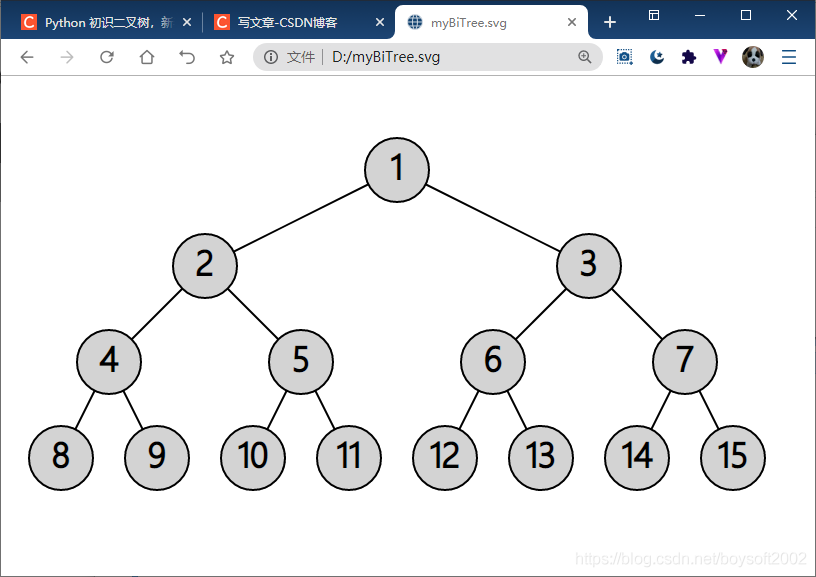
6. .svg() 二叉树的矢量图
>>> root.svg()
'\n<svg width="384" height="240" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">\n<style>
\n .value {\n font: 300 16px sans-serif;\n text-align: center;
\n dominant-baseline: middle;\n text-anchor: middle;\n }
\n .node {\n fill: lightgray;\n stroke-width: 1;\n }
\n</style>\n<g stroke="#000000">\n ...... ...... 略去N行
>>>
>>> f = open('d:\\myBiTree.svg','w')
>>> f.write(root.svg())
2434
>>> f.close()
>>> 可以输出后缀为.svg 的文本文件,一种矢量图的超文本表达文件,大部分浏览器可以直接查看;也可下载 Inkscape 等软件来编辑。输出效果如下:
7. .clone() 克隆一棵二叉树的全部或者部分
>>> from binarytree import tree
>>> a = tree()
>>> a.pprint()
____13______
/ \
____2 __14
/ \ / \
12 0 6 11
\ \ / \ \
10 4 8 9 3
>>> b = a.clone()
>>> b.pprint()
____13______
/ \
____2 __14
/ \ / \
12 0 6 11
\ \ / \ \
10 4 8 9 3
>>> c = b.right.clone()
>>> c.pprint()
__14
/ \
6 11
/ \ \
8 9 3
>>> 8. .validate() 判断二叉树是否有效,正常返回None,有三种情况会抛出相应错误:
NodeTypeError: 如果节点不是Node(i)
NodeValueError: 如果节点值不是数字,如Node(i)中的参数i不为int或float
noderReferenceError: 如果二叉树中存在对节点的循环引用
随机二叉树函数 tree()
指定层数,随机创建一棵二叉树。
函数原型:tree(height: int = 3, is_perfect: bool = False)
两个参数:层数height, 范围 0 ~ 9,最多创建 9 层,缺省值 3
是否满二叉树is_perfect,缺省值False,即非满二叉树
创建几个随机二叉树吧:
>>> import binarytree as bt
>>> a=bt.tree()
>>> a.pprint()
_8____
/ \
10 __3___
/ / \
7 4 _6
/ \ / \
1 9 12 14
>>> b=bt.tree(4)
>>> b.pprint()
____________8______
/ \
______30________ ____4__
/ \ / \
____5___ ___17 10 1___
/ \ / \ / \
_22 _28 _7 19 0 _6
/ \ / / \ /
20 12 18 23 15 13
>>> c=bt.tree(is_perfect=True)
>>> c.pprint()
_______12______
/ \
____2___ __14__
/ \ / \
13 _0 5 6
/ \ / \ / \ / \
8 11 10 9 7 3 1 4
>>> a.height,b.height,c.height
(3, 4, 3)
>>> a.levels
[[Node(8)],
[Node(10), Node(3)],
[Node(7), Node(4), Node(6)],
[Node(1), Node(9), Node(12), Node(14)]
]
>>> len(a.levels)
4
>>> # 注意: 层数levels = .height 1创建一个3层随机的满二叉树,再用正整数序列赋值到每个节点
>>> from binarytree import tree
>>> root = tree(is_perfect=True)
>>> root.pprint()
________5________
/ \
__9___ ____12__
/ \ / \
0 _13 11 4
/ \ / \ / \ / \
1 6 10 2 3 14 8 7
>>> tmpAssign = [exec(f'root[{i-1}].val={i}') for i in range(1,16)]
>>> root.pprint()
________1________
/ \
__2___ ___3___
/ \ / \
4 _5 _6 _7
/ \ / \ / \ / \
8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
>>> [i.value for i in root]
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]
>>> root[0],root[0].value
(Node(1), 1)
>>> root[1],root[1].value
(Node(2), 2)
>>> root[2];root[2].value
Node(3)
3
>>> root[14];root[14].value
Node(15)
15
>>> 或者其它层数的:
import binarytree as bt
Levels = 3
t = bt.tree(Levels-1, is_perfect=True)
for i in range(2**Levels-1):
t[i].val = i 1
t.pprint()
L = 4
a = bt.tree(L-1, is_perfect=True)
lst = [*range(1,2**L)]
for i,n in enumerate(lst):
a[i].val = n
a.pprint()
L = 5
b = bt.tree(L-1, is_perfect=True)
for i,n in enumerate([*range(1,len(b) 1)]):
b[i].val = n
b.pprint()
'''
__1__
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7
________1________
/ \
__2___ ___3___
/ \ / \
4 _5 _6 _7
/ \ / \ / \ / \
8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
____________________1____________________
/ \
________2_________ _________3_________
/ \ / \
___4___ ____5___ ____6___ ____7___
/ \ / \ / \ / \
_8 _9 _10 _11 _12 _13 _14 _15
/ \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \
16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
'''给满二叉树“仿房间号”赋值:
import binarytree as bt
Level = 6
t = bt.tree(Level-1, is_perfect=True)
for i in range(Level):
for j in range(2**i):
n = 2
#n = len(str(2**i)) 1
t[2**i j-1].val=(i 1)*10**n j 1
t.pprint()
'''
_____________________________________________________________101_____________________________________________________________
/ \
_____________________________201_____________________________ _____________________________202_____________________________
/ \ / \
_____________301_____________ _____________302_____________ _____________303_____________ _____________304_____________
/ \ / \ / \ / \
_____401_____ _____402_____ _____403_____ _____404_____ _____405_____ _____406_____ _____407_____ _____408_____
/ \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \
_501_ _502_ _503_ _504_ _505_ _506_ _507_ _508_ _509_ _510_ _511_ _512_ _513_ _514_ _515_ _516_
/ \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \
601 602 603 604 605 606 607 608 609 610 611 612 613 614 615 616 617 618 619 620 621 622 623 624 625 626 627 628 629 630 631 632
'''用指定列表赋值给满二叉树:
>>> from binarytree import tree
>>> data = [15,0,7,2,6,4,3,1,5,6,7,9,34,23,8]
>>> root = tree(is_perfect=True)
>>> root.pprint()
_______10______
/ \
___8___ __12___
/ \ / \
14 _1 4 _3
/ \ / \ / \ / \
5 2 13 9 0 6 11 7
>>> tmpAssign = [exec(f'root[{i}].val={n}') for i,n in enumerate(data)]
>>> root.pprint()
______15_______
/ \
__0__ ___7___
/ \ / \
2 6 4 _3
/ \ / \ / \ / \
1 5 6 7 9 34 23 8
>>> [i.value for i in root] == data
True
>>> 给非满二叉树赋值:
>>> from binarytree import tree
>>> root = tree()
>>> root.pprint()
_________13__
/ \
14__ 3__
\ / \
11 9 0
/ \ / \
5 10 2 6
>>> [exec(f'root[{i}].val={n}') for i,n in enumerate([*range(1,16)])]
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#237>", line 1, in <module>
[exec(f'root[{i}].val={n}') for i,n in enumerate([*range(1,16)])]
File "<pyshell#237>", line 1, in <listcomp>
[exec(f'root[{i}].val={n}') for i,n in enumerate([*range(1,16)])]
File "<string>", line 1, in <module>
File "D:\Python38-32\lib\site-packages\binarytree\__init__.py", line 350, in __getitem__
raise NodeNotFoundError("node missing at index {}".format(index))
binarytree.exceptions.NodeNotFoundError: node missing at index 3
>>> root[2]
Node(3)
>>> root[3]
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#238>", line 1, in <module>
root[3]
File "D:\Python38-32\lib\site-packages\binarytree\__init__.py", line 350, in __getitem__
raise NodeNotFoundError("node missing at index {}".format(index))
binarytree.exceptions.NodeNotFoundError: node missing at index 3
>>> root[4]
Node(11)
>>> 使用上面用到过的办法来“依葫芦画瓢”,结果程序出错。
原因在于:非满二叉树相对于满二叉树“缺失”的节点索引号是跳空的。
正如上面的测试所示:root[2],root[4]之间的 root[3]并不存在。代码修改如下:
>>> from binarytree import tree
>>> root = tree()
>>> root.pprint()
______5__
/ \
13___ 0__
/ \ / \
_3 _6 7 12
/ / / \
10 14 9 2
>>> 15 - len(root)
4 # 比满树少4个节点
>>> for i in range(15):
try:
root[i].val=i 1
except:
pass
>>> root.pprint()
_____1__
/ \
2___ 3___
/ \ / \
4 _5 6 _7
/ / / \
8 10 14 15
>>> # 跳空:9 11 12 13
>>> 续上面的节点结构,重新赋值使得层序遍历出的数值连续:
>>> t = 0
>>> for i in range(15):
try:
t =1
root[i].val=t
except:
t-=1
>>> root.pprint()
____1__
/ \
2__ 3___
/ \ / \
4 5 6 _7
/ / / \
8 9 10 11
>>> [i.value for i in root]
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]
>>> root.levelorder
[Node(1), Node(2), Node(3), Node(4), Node(5), Node(6),
Node(7), Node(8), Node(9), Node(10), Node(11)]
>>> 用列表创建二叉树的函数 build()
函数原型:build(values: List[Union[float, int]])
一个参数:实数组成的列表
上面操练Node(),tree()函数时,都练习过用指定列表给二叉树赋值。那只是为了操练而操练的,因为用build()函数非常方便,一步到位:
>>> from binarytree import build
>>> root = build([*range(1,16)])
>>> root.pprint()
________1________
/ \
__2___ ___3___
/ \ / \
4 _5 _6 _7
/ \ / \ / \ / \
8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
>>> 列表元素个数少于节点数时,后面的叶子自动为空:
>>> from binarytree import build
>>> root = build([*range(1,10)])
>>> root.pprint()
__1__
/ \
__2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7
/ \
8 9
>>> 树中间的节点为空,只要把列表对应的元素置为None:
>>> from binarytree import build
>>> data = [15,0,7,2,6,4,None,1,5,8,9,None,10]
>>> root = build(data)
>>> root.pprint()
______15_____
/ \
__0__ ___7
/ \ /
2 6 4
/ \ / \ \
1 5 8 9 10
>>> 注:给定列表的0号索引的元素一定不能为空,根节点为空列表之后元素将无处安放。另外已经置空的节点下的对应索引号也要置为None,如上面的root根节点下没 root.right.right 节点的, 所以如果要给data增加非None元素的话,程序也会出错。测试代码如下:
>>> from binarytree import build
>>> data = [15,0,7,2,6,4,None,1,5,8,9,None,10] [3]
>>> build(data)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#7>", line 1, in <module>
build(data)
File "D:\Python\lib\site-packages\binarytree\__init__.py", line 2132, in build
raise NodeNotFoundError(
binarytree.exceptions.NodeNotFoundError: parent node missing at index 6
>>>
>>> # 正确的元素添加,如下: 空索引的地方相应插入None
>>>
>>> data = [15,0,7,2,6,4,None,1,5,8,9,None,10]
>>> data = [None,None,3,11,12,13,14,16,17,18,None,None,19,20]
>>> root = build(data)
>>> root.pprint()
__________________15___________
/ \
________0________ _________7
/ \ /
___2___ ___6___ 4___
/ \ / \ \
1 _5 _8 _9 _10
/ \ / \ / \ / \ / \
3 11 12 13 14 16 17 18 19 20
>>> build2()
用法基本与build()相同,但它的参数允许更紧凑的列表,因为它的同一层节点中如果最后连续为空只要一个“None”。两者的区别有点像上面在二叉树方法属性一节里提到的(已红色标注):values 和 values2的区别。请看如下测试代码:
>>> root1 = build([2, 5, None,3,None,None, None, 1, 4])
>>> root1.pprint()
2
/
__5
/
3
/ \
1 4
>>> # build()能用的列表,build2()不一定通用:
>>> root1 = build2([2, 5, None,3,None,None, None, 1, 4])
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#10>", line 1, in <module>
root1 = build2([2, 5, None,3,None,None, None, 1, 4])
File "D:\Python\lib\site-packages\binarytree\__init__.py", line 2194, in build2
node = queue.popleft()
IndexError: pop from an empty deque
>>>
>>> # build2()正确的列表参数:
>>> root2 = build2([2, 5, None,3,None, 1, 4])
>>> root2.pprint()
2
/
__5
/
3
/ \
1 4
>>> bst() heap()
用法基本上与 tree() 相同,参数也是:层数(0~9); is_perfect = False(默认值)
返回值:分别是特殊的二叉树 bst 和 heap;另heap()多一个参数 is_max = True(默认值)
>>> from binarytree import bst
>>> root = bst()
>>> root.height
3
>>> root.is_bst
True
>>> root.pprint()
10______
/ \
__8 ____14
/ /
6 12
/ \ \
4 7 13
>>>
>>> from binarytree import heap
>>> root = heap()
>>> root.height
3
>>> root.is_max_heap
True
>>> root.pprint()
________14____
/ \
__12__ 11
/ \ / \
8 10 3 9
/ \ / \ /
0 4 6 1 2
>>>
>>> root = heap(4, is_max=False)
>>> root.height
4
>>> root.is_min_heap
True
>>>
>>> root = heap(5, is_max=False, is_perfect=True)
>>> root.height
5
>>> root.is_min_heap
True
>>> root.is_perfect
Truetree() 也能造出bst 和 heap 来,只是用循环来多花点时间:
>>> from binarytree import bst, heap
>>> bst1 = tree()
>>> while not bst1.is_bst:
bst1 = tree()
>>> bst1.pprint()
1____
\
__14
/
2
\
5
>>> heap1 = tree()
>>> while not heap1.is_max_heap:
heap1 = tree()
>>> heap1.pprint()
________14_____
/ \
__12__ _13
/ \ / \
6 10 11 3
/ \ / \ /
2 0 1 4 9
>>> heap2 = tree()
>>> while not heap2.is_min_heap:
heap2 = tree()
>>> heap2.pprint()
________0___
/ \
__3___ _1
/ \ / \
7 _4 11 2
/ \ / \
9 8 10 13
>>> 获取双亲节点函数 get_parent()
get_parent(root: binarytree.Node, child: binarytree.Node)
给定子节点,返回它在根节点下的上一层级的节点
>>> from binarytree import tree, get_parent
>>> root = tree()
>>> print(root)
______8__
/ \
7 1
/ \ /
6 10 5
/ \
9 11
>>> print(get_parent(root,root.left.left))
7
/ \
6 10
/ \
9 11
>>> get_parent(root,root.left.left) == get_parent(root,root.left.right)
True
>>> 总结
到此这篇关于Python初识二叉树续之实战binarytree的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python实战binarytree内容请搜索Devmax以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持Devmax!