今天来和小伙伴们聊一聊 Spring Security 中的异常处理机制。
在 Spring Security 的过滤器链中,ExceptionTranslationFilter 过滤器专门用来处理异常,在 ExceptionTranslationFilter 中,我们可以看到,异常被分为了两大类:认证异常和授权异常,两种异常分别由不同的回调函数来处理,今天就来和大家分享一下这里的条条框框。
1.异常分类
Spring Security 中的异常可以分为两大类,一种是认证异常,一种是授权异常。
认证异常就是 AuthenticationException,它有众多的实现类:
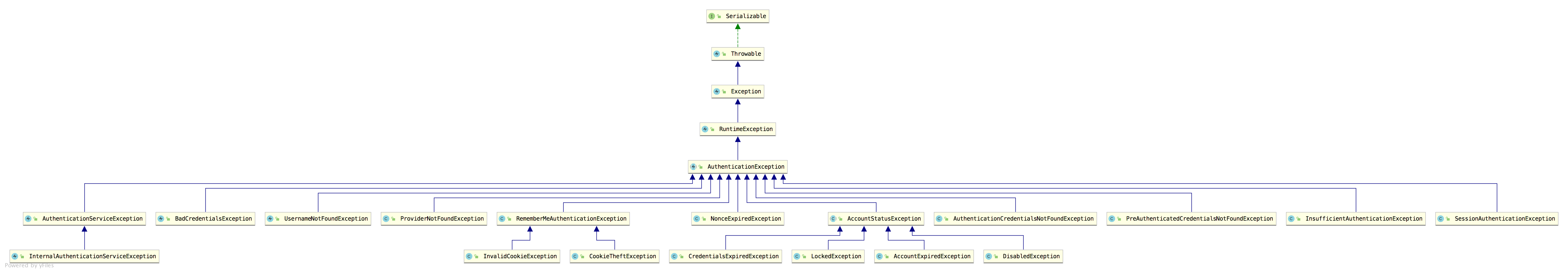
可以看到,这里的异常实现类还是蛮多的,都是都是认证相关的异常,也就是登录失败的异常。这些异常,有的松哥在之前的文章中都和大家介绍过了,例如下面这段代码
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter();
RespBean respBean = RespBean.error(e.getMessage());
if (e instanceof LockedException) {
respBean.setMsg("账户被锁定,请联系管理员!");
} else if (e instanceof CredentialsExpiredException) {
respBean.setMsg("密码过期,请联系管理员!");
} else if (e instanceof AccountExpiredException) {
respBean.setMsg("账户过期,请联系管理员!");
} else if (e instanceof DisabledException) {
respBean.setMsg("账户被禁用,请联系管理员!");
} else if (e instanceof BadCredentialsException) {
respBean.setMsg("用户名或者密码输入错误,请重新输入!");
}
out.write(new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(respBean));
out.flush();
out.close();
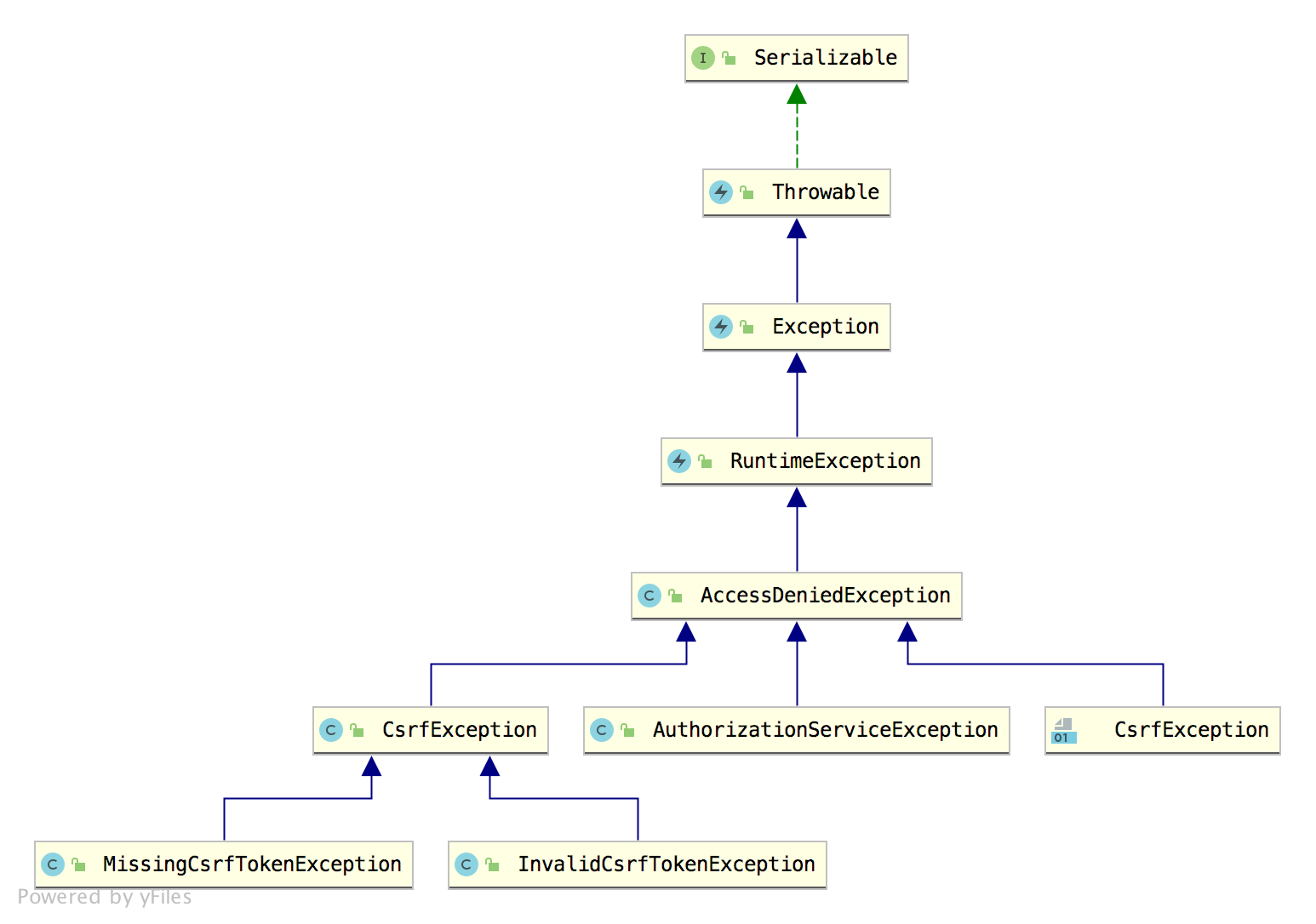
另一类就是授权异常 AccessDeniedException,授权异常的实现类比较少,因为授权失败的可能原因比较少。
2.ExceptionTranslationFilter
ExceptionTranslationFilter 是 Spring Security 中专门负责处理异常的过滤器,默认情况下,这个过滤器已经被自动加载到过滤器链中。
有的小伙伴可能不清楚是怎么被加载的,我这里和大家稍微说一下。
当我们使用 Spring Security 的时候,如果需要自定义实现逻辑,都是继承自 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 进行扩展,WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 中本身就进行了一部分的初始化操作,我们来看下它里边 HttpSecurity 的初始化过程:
protected final HttpSecurity getHttp() throws Exception {
if (http != null) {
return http;
}
AuthenticationEventPublisher eventPublisher = getAuthenticationEventPublisher();
localConfigureAuthenticationBldr.authenticationEventPublisher(eventPublisher);
AuthenticationManager authenticationManager = authenticationManager();
authenticationBuilder.parentAuthenticationManager(authenticationManager);
Map<Class<?>, Object> sharedObjects = createSharedObjects();
http = new HttpSecurity(objectPostProcessor, authenticationBuilder,
sharedObjects);
if (!disableDefaults) {
http
.csrf().and()
.addFilter(new WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter())
.exceptionHandling().and()
.headers().and()
.sessionManagement().and()
.securityContext().and()
.requestCache().and()
.anonymous().and()
.servletApi().and()
.apply(new DefaultLoginPageConfigurer<>()).and()
.logout();
ClassLoader classLoader = this.context.getClassLoader();
List<AbstractHttpConfigurer> defaultHttpConfigurers =
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(AbstractHttpConfigurer.class, classLoader);
for (AbstractHttpConfigurer configurer : defaultHttpConfigurers) {
http.apply(configurer);
}
}
configure(http);
return http;
}
可以看到,在 getHttp 方法的最后,调用了 configure(http);,我们在使用 Spring Security 时,自定义配置类继承自 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 并重写的 configure(HttpSecurity http) 方法就是在这里调用的,换句话说,当我们去配置 HttpSecurity 时,其实它已经完成了一波初始化了。
在默认的 HttpSecurity 初始化的过程中,调用了 exceptionHandling 方法,这个方法会将 ExceptionHandlingConfigurer 配置进来,最终调用 ExceptionHandlingConfigurer#configure 方法将 ExceptionTranslationFilter 添加到 Spring Security 过滤器链中。
我们来看下 ExceptionHandlingConfigurer#configure 方法源码:
@Override
public void configure(H http) {
AuthenticationEntryPoint entryPoint = getAuthenticationEntryPoint(http);
ExceptionTranslationFilter exceptionTranslationFilter = new ExceptionTranslationFilter(
entryPoint, getRequestCache(http));
AccessDeniedHandler deniedHandler = getAccessDeniedHandler(http);
exceptionTranslationFilter.setAccessDeniedHandler(deniedHandler);
exceptionTranslationFilter = postProcess(exceptionTranslationFilter);
http.addFilter(exceptionTranslationFilter);
}
可以看到,这里构造了两个对象传入到 ExceptionTranslationFilter 中:
- AuthenticationEntryPoint 这个用来处理认证异常。
- AccessDeniedHandler 这个用来处理授权异常。
具体的处理逻辑则在 ExceptionTranslationFilter 中,我们来看一下:
public class ExceptionTranslationFilter extends GenericFilterBean {
public ExceptionTranslationFilter(AuthenticationEntryPoint authenticationEntryPoint,
RequestCache requestCache) {
this.authenticationEntryPoint = authenticationEntryPoint;
this.requestCache = requestCache;
}
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
try {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
Throwable[] causeChain = throwableAnalyzer.determineCauseChain(ex);
RuntimeException ase = (AuthenticationException) throwableAnalyzer
.getFirstThrowableOfType(AuthenticationException.class, causeChain);
if (ase == null) {
ase = (AccessDeniedException) throwableAnalyzer.getFirstThrowableOfType(
AccessDeniedException.class, causeChain);
}
if (ase != null) {
if (response.isCommitted()) {
throw new ServletException("Unable to handle the Spring Security Exception because the response is already committed.", ex);
}
handleSpringSecurityException(request, response, chain, ase);
}
else {
if (ex instanceof ServletException) {
throw (ServletException) ex;
}
else if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
}
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}
private void handleSpringSecurityException(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, RuntimeException exception)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if (exception instanceof AuthenticationException) {
sendStartAuthentication(request, response, chain,
(AuthenticationException) exception);
}
else if (exception instanceof AccessDeniedException) {
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
if (authenticationTrustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication) || authenticationTrustResolver.isRememberMe(authentication)) {
sendStartAuthentication(
request,
response,
chain,
new InsufficientAuthenticationException(
messages.getMessage(
"ExceptionTranslationFilter.insufficientAuthentication",
"Full authentication is required to access this resource")));
}
else {
accessDeniedHandler.handle(request, response,
(AccessDeniedException) exception);
}
}
}
protected void sendStartAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain,
AuthenticationException reason) throws ServletException, IOException {
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(null);
requestCache.saveRequest(request, response);
logger.debug("Calling Authentication entry point.");
authenticationEntryPoint.commence(request, response, reason);
}
}
ExceptionTranslationFilter 的源码比较长,我这里列出来核心的部分和大家分析:
- 过滤器最核心的当然是 doFilter 方法,我们就从 doFilter 方法看起。这里的 doFilter 方法中过滤器链继续向下执行,ExceptionTranslationFilter 处于 Spring Security 过滤器链的倒数第二个,最后一个是 FilterSecurityInterceptor,FilterSecurityInterceptor 专门处理授权问题,在处理授权问题时,就会发现用户未登录、未授权等,进而抛出异常,抛出的异常,最终会被 ExceptionTranslationFilter#doFilter 方法捕获。
- 当捕获到异常之后,接下来通过调用
throwableAnalyzer.getFirstThrowableOfType方法来判断是认证异常还是授权异常,判断出异常类型之后,进入到 handleSpringSecurityException 方法进行处理;如果不是 Spring Security 中的异常类型,则走 ServletException 异常类型的处理逻辑。 - 进入到 handleSpringSecurityException 方法之后,还是根据异常类型判断,如果是认证相关的异常,就走 sendStartAuthentication 方法,最终被 authenticationEntryPoint.commence 方法处理;如果是授权相关的异常,就走 accessDeniedHandler.handle 方法进行处理。
AuthenticationEntryPoint 的默认实现类是 LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint,因此默认的认证异常处理逻辑就是 LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint#commence 方法,如下:
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException {
String redirectUrl = null;
if (useForward) {
if (forceHttps && "http".equals(request.getScheme())) {
redirectUrl = buildHttpsRedirectUrlForRequest(request);
}
if (redirectUrl == null) {
String loginForm = determineUrlToUseForThisRequest(request, response,
authException);
RequestDispatcher dispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher(loginForm);
dispatcher.forward(request, response);
return;
}
}
else {
redirectUrl = buildRedirectUrlToLoginPage(request, response, authException);
}
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, redirectUrl);
}
可以看到,就是重定向,重定向到登录页面(即当我们未登录就去访问一个需要登录才能访问的资源时,会自动重定向到登录页面)。
AccessDeniedHandler 的默认实现类则是 AccessDeniedHandlerImpl,所以授权异常默认是在 AccessDeniedHandlerImpl#handle 方法中处理的:
public void handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) throws IOException,
ServletException {
if (!response.isCommitted()) {
if (errorPage != null) {
request.setAttribute(WebAttributes.ACCESS_DENIED_403,
accessDeniedException);
response.setStatus(HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN.value());
RequestDispatcher dispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher(errorPage);
dispatcher.forward(request, response);
}
else {
response.sendError(HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN.value(),
HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN.getReasonPhrase());
}
}
}
可以看到,这里就是服务端跳转返回 403。
3.自定义处理
前面和大家介绍了 Spring Security 中默认的处理逻辑,实际开发中,我们可以需要做一些调整,很简单,在 exceptionHandling 上进行配置即可。
首先自定义认证异常处理类和授权异常处理类:
@Component
public class MyAuthenticationEntryPoint implements AuthenticationEntryPoint {
@Override
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException {
response.getWriter().write("login failed:" authException.getMessage());
}
}
@Component
public class MyAccessDeniedHandler implements AccessDeniedHandler {
@Override
public void handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) throws IOException, ServletException {
response.setStatus(403);
response.getWriter().write("Forbidden:" accessDeniedException.getMessage());
}
}
然后在 SecurityConfig 中进行配置,如下:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
...
...
.and()
.exceptionHandling()
.authenticationEntryPoint(myAuthenticationEntryPoint)
.accessDeniedHandler(myAccessDeniedHandler)
.and()
...
...
}
}
配置完成后,重启项目,认证异常和授权异常就会走我们自定义的逻辑了。
到此这篇关于一文搞懂Spring Security异常处理机制的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Spring Security异常处理内容请搜索Devmax以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持Devmax!